Data Space Pathway
Have a look at the Data Space Pathway Introduction Video here below!
(We recommend viewing in HD. Click on YouTube or click here to view on You Tube)
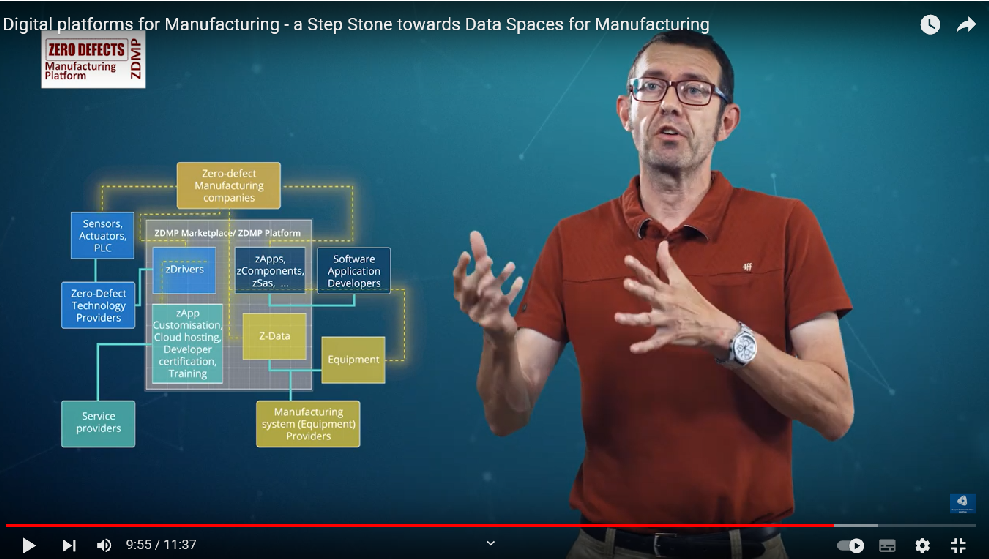
Also check out the Digital Platforms Use Cases Video, showcasing the step stones to implementing Data Spaces in Manufacturing
(We recommend viewing in HD. Click on YouTube or click here to view on You Tube)
The Data Space pathway of the Connected Factories project provides a conceptual and operational framework where manufacturing companies could position themselves and their industrial cases with respect to a more mature and aware take-up and exploitation of the Data they produce.
Data Spaces represent one of the fundamental enablers, allowing the full exploitation of Data Economy business models of Open Data, Data Marketplaces and Trusted Data Ecosystems. For instance, in a Smart Autonomous Factories scenario, Data Spaces support dynamic multi-stakeholder industrial assets monitoring and control, enabling predictive maintenance and substantial reduction of environmental footprint. In a Collaborative Product-Service scenario, Data Spaces (often associated to Digital Product Passports) are able to collect, integrate and harmonise highly distributed datasets, in space and in time, along the whole lifecycle of the product, enabling new service-oriented business. In a Hyperconnected Factories scenario, Data Spaces are able to model heterogeneous, complex and dynamic supply and delivery business ecosystems by adopting common standard data models and business processes, finally enabling order-capacity matchmaking and One-of-a-Kind production.
The Data Space pathway is composed of 5 levels, characterised by increasing maturity degrees of the manufacturing company / industrial case towards a full exploitation of Data Economy in Manufacturing.
At Level I, data remain trapped inside the systems and is practically not available to Manufacturing Industry end users and further elaborations. At Level II, traditional Enterprise Systems (SCADA MES ERP PLM SCM) are able to capture most of the data produced, but owing to scarce adoption of open standards, data silos are created so that processing and analytics is just possible from inside such applications. At Level III, ad-hoc data integration bridges are created among systems and their repositories, but every integration project remains isolated and needs to start from scratch.
We start speaking of Data Spaces at Level IV of the pathway’s scale, named Interoperability. At this level, the Technology perspective to Data Spaces is addressed. As an integral part of common unified Industrial Architecture Models (like the OPC Unified Architecture), Findable Accessible Interoperable and Re-usable Data Sets are implemented thanks to open standard data models (like the RAMI Asset Administration Shell) and semantic interoperability (like the Industrial Ontology Foundry);
Industrial Data Platforms are able to integrate, process, analyse, visualise and share the data in secure and trusted manner Advanced rule- and AI-based decision support systems implement the business and governance agreements and let the ecosystem work and evolve along time.
In conjunction with the Level IV Technical approach, Level V of the Data Spaces pathway addresses the Business challenges implied by the implementation of Data Spaces. Three main Business Models are enabled: Open Data, Data Marketplace and Trusted Network.
The evolution of Data Aggregation, Data Anonymisation and above all synthetic Data Generation techniques as well as the flourishing of open innovation business models is opening new interesting perspectives for Manufacturing Open Data development.