Autonomous & Smart Factories Pathway
This pathway focuses on digitalisation within the so-called ‘Automation Pyramid’.
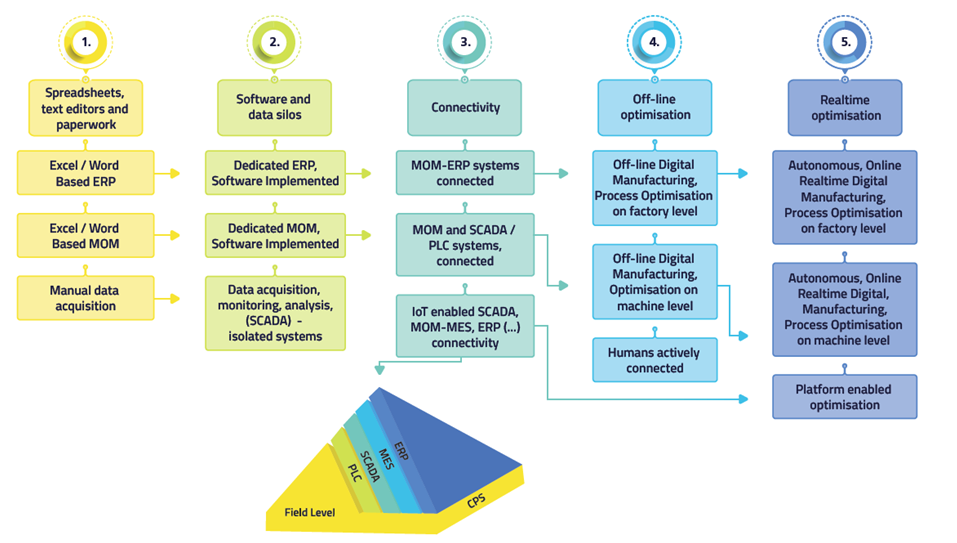
In this pathway, Level 1 reflects a situation that is still a reality in many manufacturing companies: data acquisition on the shop floor is done predominantly manually, while spreadsheets and text editors are used to do Enterprise Resource Planning (or ERP) and Manufacturing Operations Management (or MOM) including scheduling (also referred to as MES, Manufacturing Execution System).
Level 2 involves the implementation of dedicated digital tools for doing ERP and MOM, while Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) solutions are implemented on shop floor level, connected to sensors and actuators and other field devices via PLCs or industrial PC’s.
Level 3 focusses on the company internal connection of ERP, MOM and SCADA-PLC levels. This connectivity will increase the awareness of Enterprise Resource Planning about the status and condition of manufacturing operations, such as possible delays due to break-down or maintenance. This level includes the introduction of Industrial connectivity approaches, such as the use of Industrial IoT, RFID, other wireless technologies or identification methods.
There are different ways to achieve connectivity, as is illustrated by the ‘IIOT connectivity stack that can be found in an Industrial Internet Consortium and Plattform Industrie 4.0 Joint Whitepaper ‘Architecture Alignment and Interoperability’ (https://www.iiconsortium.org/pdf/JTG2_Whitepaper_final_20171205.pdf)
In level 3 and beyond, the concept of Cyber-Physical systems is relevant, leading to a less hierarchical interpretation of the Automation Pyramid.
Level 4 focuses on the implementation of more advanced optimisation approaches, either on factory level or on machine level. Another achievement in this level is the inclusion of humans in the digital information or connectivity loop.
In Level 5, optimisation can be done in real time on factory or machine level. The deployment of digital platforms for manufacturing is situated on this level.
Deliverable 4.7 reflects a snapshot at the end of December 2019 of the progress and outlook of the development of the pathways. It is available for download here.
Watch: Introduction to Pathways
(We recommend viewing in HD. Click on YouTube to view in full screen)
The Autonomous Smart Factory pathway was the focus of the video ‘Introduction to the pathways to digitalisation in manufacturing’ that was launched prior to the ICT2018 conference in Vienna on 4-6 December 2018.
In that video the results and demonstrator case of the FAR-EDGE project was used to illustrate to pathway. An interesting point (highlighted in the presentation of FAR-EDGE in the ConnectedFactories session at ICT2018 on 5 December in Vienna), is that The Wirhpool case in FAR-EDGE would actually ‘bridge’ level 4, by applying simulation, making that real-time optimisation would be implemented on the factory floor after virtual ‘offline’ testing. (see also this presentation from ICT 2018 )
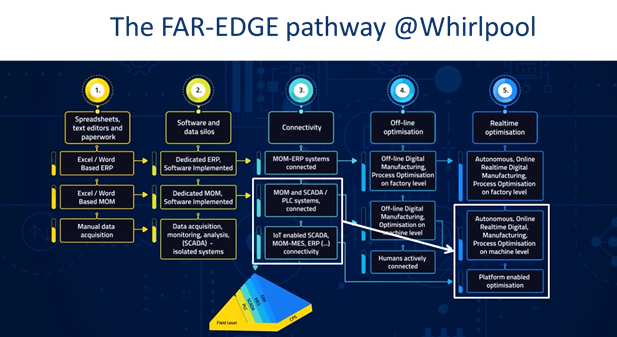
Projects, project results and demonstrators are described and positioned on the pathways via the EFFRA Innovation Portal. See below how the project FAR-EDGE is currently positioned on the pathways 'Autonomous Smart Factories'
First in the 'List' view:
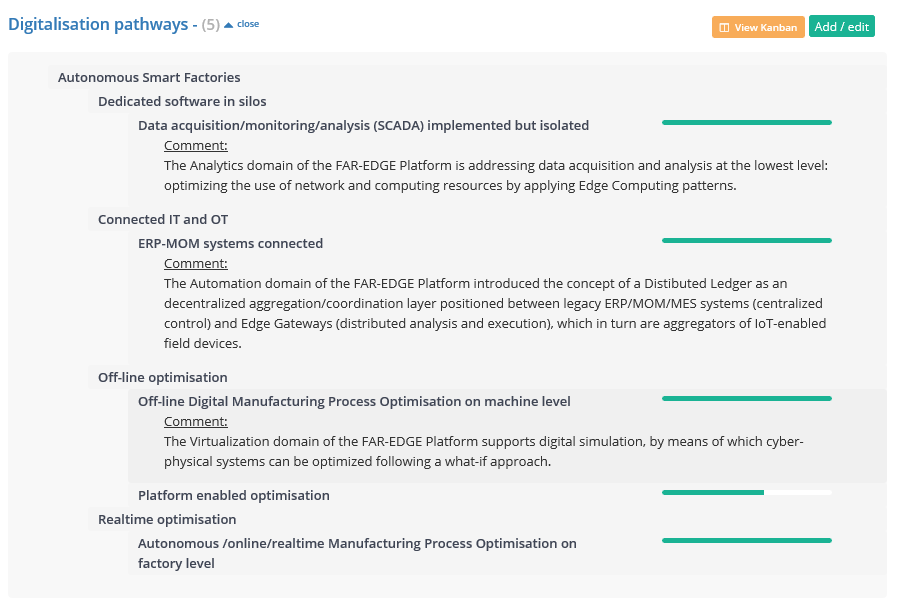
In the 'Kanban' view:

Please see here for more information about how you can share your projects and cases and position these on the pathways.
