Cybersecurity pathway
The first 5 levels of CyberSecurity Pathway were developed with a perspective of manufacturing companies and developers of digital manufacturing platforms with different sets of skills, competences, technical capabilities – overall an appreciation of the level of maturity.
Without the intention to categorise or to classify any specific platform, system or company, the intention is to support entities to ensure they can try to meet a number of basic cybersecurity capabilities. Instead of trying to achieve a maximum from the start, which without a reasonable risk and cyber-risk assessment, would not be highly effective, the components indicate some fundamental cyber hygiene. The pathway doesn’t even consider whether systems are fully connected, or what level of complexity they are executing.
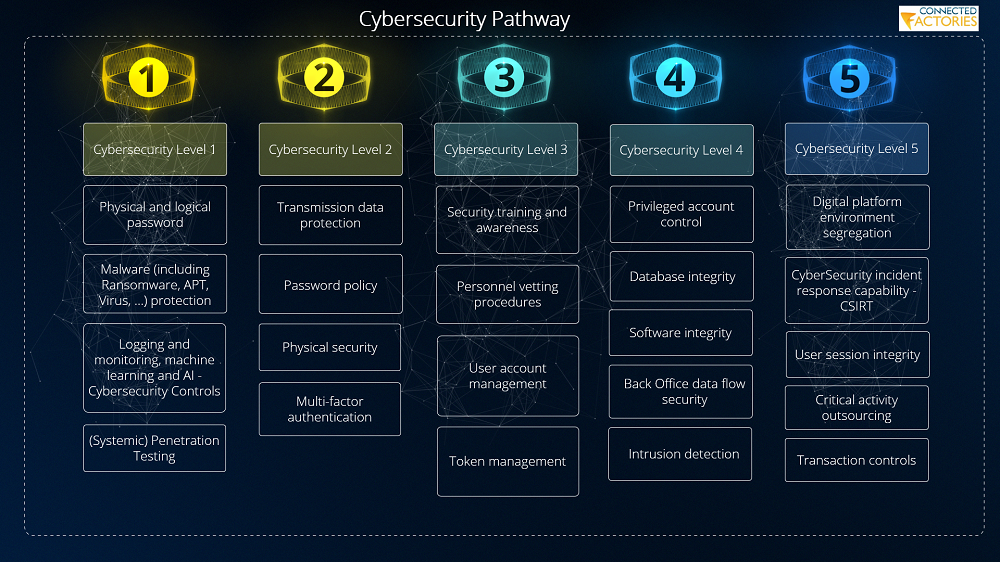
The pathway was derived out of different interviews and workshop with multiple manufacturing companies and platform developers, both from industry and research (the FOF-11-projects) and resulted in a structured guidance of a series of components that classify the necessity of CyberSecurity mechanisms to put in place. As it is a Pathway - a guided lightning path - it refrains from being patronizing and instructive, rather than encouraging and stimulating. Even with the different colors, indicating the absolute necessities to be put in place (on the far left) such as physical and logical password / access and the logging and monitoring as basic fundamentals that will return with either environment where it is finally being put into operation.
While it is built upon existing standards such as ISO27k, IEC62443 and different other de-facto and industry cybersecurity standards and regulatory requirements for CyberSecurity in manufacturing and industrial environments, it is not intended to be a complicated approach but rather a simplified technological perspective of requirements. Finally, the CyberSecurity Pathway provides guidance on further improvements and next steps; on which the Connected Factories 2 Pathway was built.
For a better understanding of all of the components related to the CyberSecurity Pathway elements, we refer to the Structured Wiki on the EFFRA portal that describes all of the individual elements of the Pathway and adds references and suggestions of technology components (example: CSIRT.- incident response capability30) that can serve as tooling to establish the Pathways.
The Connected Factories 2 CyberSecurity Pathway builds on top of these, and still expects manufacturing companies large and small, Digital Manufacturing Platform developers from research up to integration to keep levels I to V of the CyberSecurity Pathway as the key instrumentation for the continuation of levels VI up to level XX. More information: D2.6_Pathways cross-fertilisation with Digital Technologies - Second Iteration (chapter 5)
(See all ConnectedFactories Deliverables here)
